Do Heat Pumps Work Well With Industrial Radiators?
This is a subtitle for your new post
In the pursuit of energy efficient and sustainable heating solutions, many businesses are exploring the integration of heat pumps with industrial radiators. Traditionally, industrial heating has relied on high-temperature boilers and fossil fuel systems, but with mounting pressure to reduce carbon footprints and cut operating costs, industries are increasingly turning toward renewable and efficient alternatives.
One promising pairing is the use of industrial radiators with heat pumps. This combination not only ensures consistent and comfortable heating, but also helps businesses meet their sustainability goals. In this article, we’ll dive deep into how heat pumps and industrial radiators work together, the benefits and challenges of integrations, and the long-term financial and environmental advantages of adopting this innovative solution.
Understanding Heat Pumps and Industrial Radiators
Before examining their compatibility, it’s important to understand each component.
What Are Heat Pumps?
Heat pumps are devices that transfer heat from one place to another using electricity. Instead of burning fuel to generate heat, they extract thermal energy from external sources like air, water, or the ground, and transfer it indoors. The main types include:
● Air-source heat pumps (ASHPs): Draw heat from the outside air.
● Ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs): Extract heat from the ground.
● Water-source heat pumps (WSHPs): Utilise nearby water sources.
These systems are known for their high efficiency - often delivering three or four units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed.
What Are Industrial Radiators?
Industrial radiators are large scale heating units designed to distribute heat across wide spaces, such as factories, warehouses and workshops. They are engineered to operate under high-demand, offering durability and performance in environments where consistent heating is crucial. Unlike standard domestic radiators, industrial versions are built to handle larger heat loads and can function effectively with different heat sources.
Why Heat Pumps Work Well With Industrial Radiators
At first glance, it can be easy to assume that heat pumps and industrial radiators are incompatible due to temperature differences. Heat pumps generally deliver lower water temperatures than traditional boilers, while industrial radiators are often thought to require high temperatures for effective performance. However, modern engineering has bridged this gap.
Improved Compatibility
● Low-temperature efficiency: Modern industrial radiators are designed with larger surface areas, enabling them to work effectively even with the lower output temperatures of heat pumps.
● Uniform heat distribution: Heat pumps deliver steady, consistent heat, which complements the radiators ability to distribute warmth across expansive industrial spaces.
Scalability
Industrial sites often have fluctuating heating needs depending on production levels or occupancy. Heat pumps, when paired with radiators, provide a scalable solution that adjusts output without excessive energy waste.
Longevity and Reliability
Industrial radiators are built for durability, and when combined with the steady operation of heat pumps (which experience less wear compared to traditional combustion systems), businesses benefit from a heating system with extended lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
Benefits of Pairing Heat Pumps with Industrial Radiators
Integrating heat pumps with industrial radiators offers a wide range of advantages:
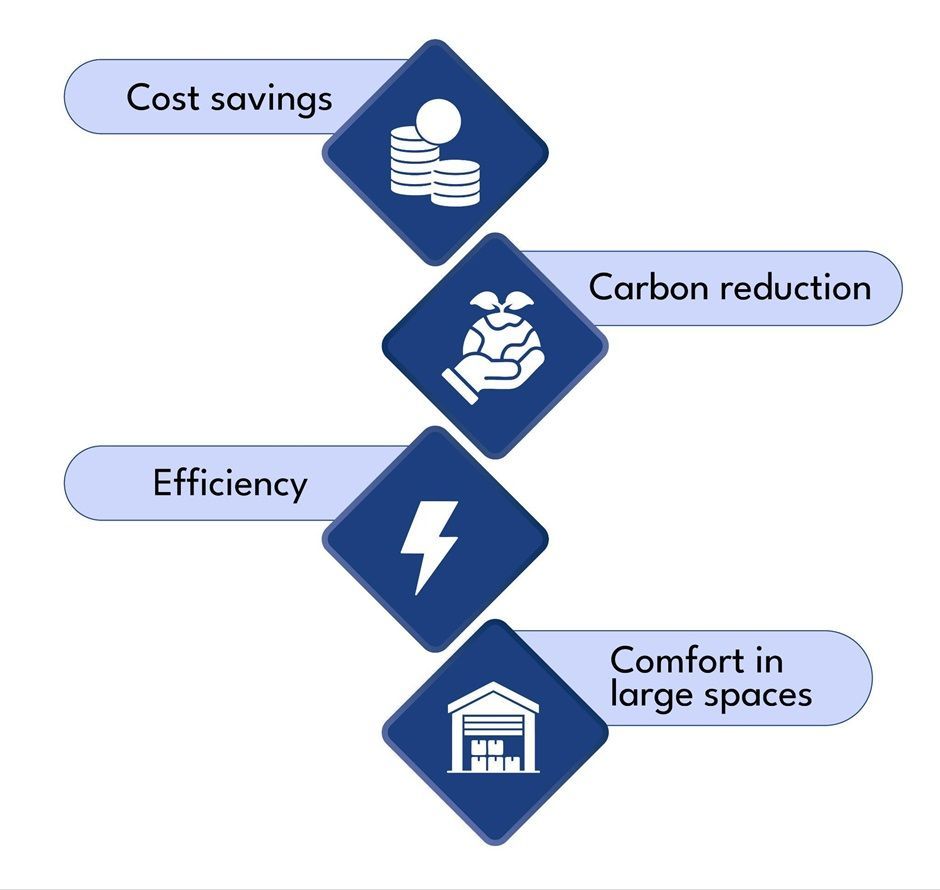
1. Energy Efficiency
Heat pumps are inherently efficient, often achieving efficiency levels of 300-400%. When paired with radiators optimised for lower flow temperatures, businesses can maximise this efficiency, drastically reducing energy consumption compared to conventional boilers.
2. Cost Savings
Although the initial investment may be higher, the operational savings are substantial. Lower energy consumption translates directly into reduced utility bills, and businesses can often access government grants or tax incentives for adopting renewable heating solutions.
3. Sustainability and Carbon Reduction
Switching from fossil-fuel based boilers to heat pumps can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When combined with industrial radiators, which efficiently distribute heat without requiring excessive temperatures, the system operates more sustainably.
4. Improved Working Conditions
Steady, even heating improves workplace comfort and productivity. Industrial radiators ensure warmth is distributed evenly, reducing cold spots and improving conditions in large facilities.
5. Future-Proofing Industrial Heating
With stricter environmental regulations and rising energy costs, investing in renewable, compatible infrastructure ensures businesses are prepared for future demands. Heat pumps and industrial radiators together create a system that meets today’s needs while staying adaptable to tomorrow’s requirements.
Challenges to Consider
While the benefits are clear, integrating heat pumps with industrial radiators does come with some challenges that businesses should weigh carefully.
Initial Investment
Heat pumps and modern industrial radiators represent significant upfront costs. However, the long-term savings in energy bills and potential government subsidies often balance this out over time.
Retrofitting Existing Systems
Older facilities may require additional modifications to accommodate lower-temperature systems, such as upgrading radiator designs or improving insulation. These retrofitting costs should be factored into the overall project.
Climate Considerations
The performance of air source heat pumps can vary with external temperatures. In extremely cold climates, supplemental heating might be necessary, though ground-source or hybrid systems can help mitigate this issue.
Space Requirements
Heat pumps, especially ground and water source types, may require substantial installation space. Businesses must assess site conditionals to determine feasibility.
Key Factors for Businesses to Consider
For companies exploring this integration, the following factors are critical:
- Building Insulation: Well-insulated spaces maximise efficiency and reduce energy waste.
- System Design: Radiators must be sized and selected for compatibility with heat pump flow temperatures.
- Energy Source: Choosing between air, ground, or water-source heat pumps depends on site conditions and energy goals.
- Financial Incentives: Explore government programs that provide grants, rebates, or tax credits for renewable heating adoption.
- Operational Demands: Assess heating loads to ensure the system can meet peak requirements without compromising efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Perhaps one of the most significant advantages of this integration is the environmental benefit. Heating accounts for a substantial portion of industrial energy consumption and carbon emissions. By switching to heat pumps supported by industrial radiators:
● CO₂ emissions are drastically reduced.
● Reliance on fossil fuels decreases
● Industries move closer to achieving net-zero goals.
This makes the system not just a financial decision, but also a critical step toward corporate sustainability and environmental responsibility.
A Future-Ready Heating Solution
The combination of heat pumps and industrial radiators represents a forward-thinking solution for businesses seeking efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible heating. While challenges exist in terms of upfront investment and retrofitting, the long-term benefits far outweigh the hurdles. From reduced energy bills to lower emissions and improved workplace comfort, this pairing is an excellent choice for industries preparing for a sustainable future.
For businesses serious about cutting costs, reducing environmental impact and future-proofing their heating systems, the message is clear: heat pumps work well with industrial radiators - and together, they create a heating solution that is both smart, and sustainable. Contact us today to find out more about efficient heating solutions.